Context: Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) are rapidly rising in India, particularly in the urban areas. Studies have shown increased risks of NCDs for women post-menopause, with a significant rise in diabetes, obesity, fatty liver, and hypertension.
What are Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs)?
1. Definition
NCDs are chronic diseases that are not caused by infectious agents.
They typically have a long development period and can persist for years or even a lifetime.
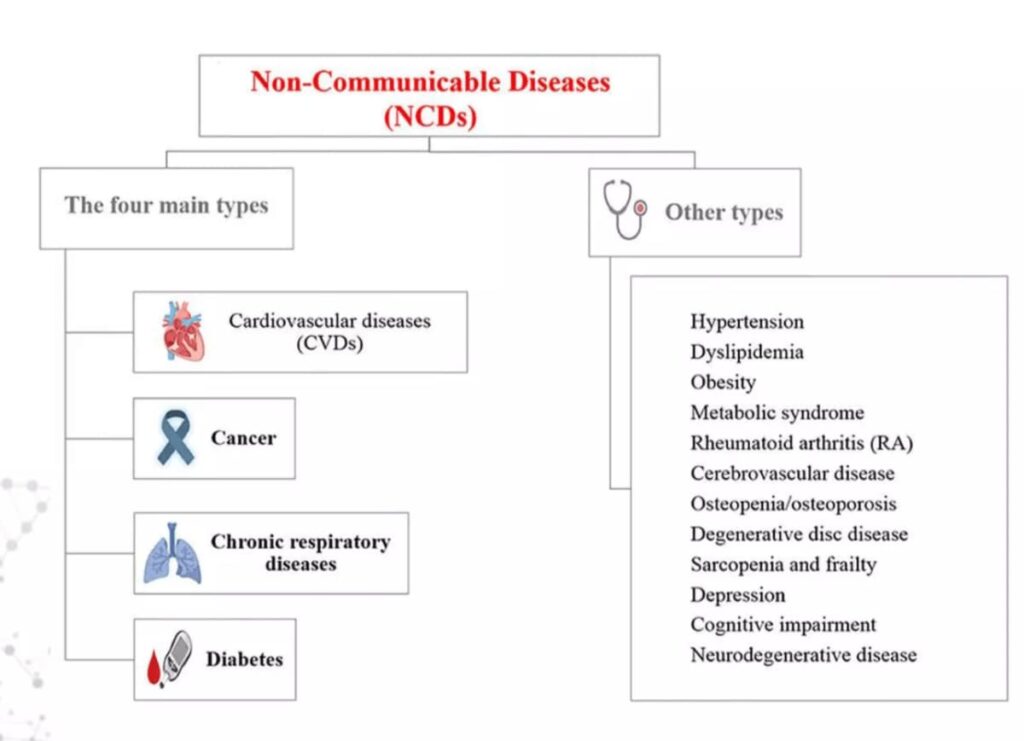
2. Types of NCDs
NCDs include a broad range of conditions such as:
Cardiovascular diseases
Cancer
Diabetes
Chronic respiratory diseases
Mental health disorders
3. Risk Factors for NCDs
Key risk factors that contribute to the development of NCDs include:
Unhealthy diets
Physical inactivity
Tobacco use
Harmful alcohol consumption
Pollution and environmental factors
4. Global and National Impact
According to the World Health Organization (WHO):
NCDs are responsible for 71% of all deaths globally.
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death among NCDs.
In India:
As per WHO’s 2022 report, 66% of total deaths in 2019 were due to NCDs.
5. Impact on Older Adults
Older adults (ages 60 and above) experience the highest rates of:
Infectious diseases
NCDs
Disability and injuries
Role of Urbanisation in Increasing the Burden of NCDs
1. Economic Structure
Urban economies are primarily service-oriented, which results in:
A reduced need for manual labor compared to rural, agrarian economies.
This leads to a sedentary lifestyle, which increases the risk of developing NCDs.
2. Changing Dietary Patterns
Urban areas often witness:
Increased consumption of processed foods, unhealthy fats, and sugars.
Poor dietary habits contribute significantly to the rising incidence of NCDs like obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
3. Environmental Factors
Pollution and the Urban Heat Island effect in cities exacerbate the health risks associated with NCDs, including respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
4. Lifestyle Choices
In urban settings, there is a higher prevalence of:
Alcohol consumption
Smoking
These behaviors significantly increase the risk of developing NCDs such as cancer, liver disease, and heart disease.
5. Family Structure Changes
The shift towards nuclear families in urban areas can lead to:
Mental health issues due to the lack of emotional support from extended family members.
Initiatives Taken by the Government to Combat NCDs
1. National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NP-CDCS)
Implemented since 2010, this program aims to prevent and control major NCDs including:
Hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, stroke, chronic kidney disease, COPD, asthma, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
2. National Action Plan
India has adopted a National Action Plan to reduce global premature deaths from NCDs by 25% by 2025.
The plan is aligned with the WHO’s Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of NCDs (2013-2020).
The UN SDG Target 3.4 aims to reduce premature mortality from NCDs by one-third by 2030 globally.
3. Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY)
Provides coverage for the treatment of NCDs, including cancer, to over 10 crore families.
4. Fit India Movement and Yoga Promotion
Encourages people to stay healthy and fit by incorporating physical activities and sports into their lifestyle.
5. National Mental Health Programme & National Tele Mental Health Programme
Aims to improve access to quality mental health counseling and care services across the country, addressing the growing mental health challenges associated with urbanization.
