CONTEXT: The recent unfortunate passing of actor Gene Hackman and his spouse Betsy Arakawa has highlighted the issue of hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS).

About Hantavirus
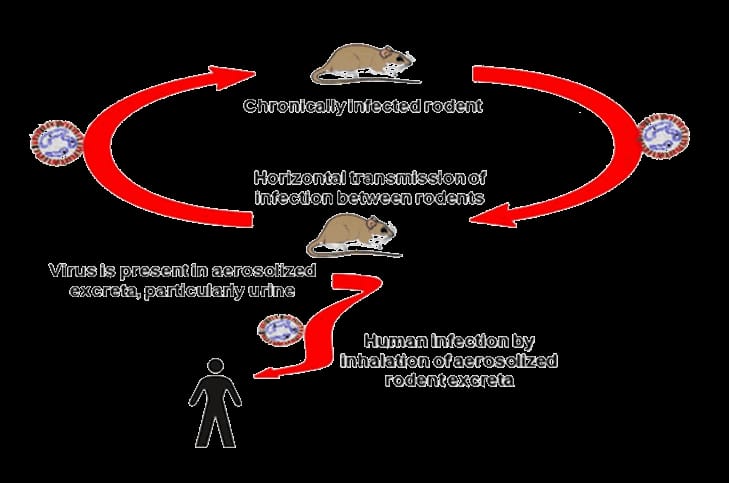
Hantavirus is a family of rodent-borne viruses that can cause severe illnesses, including respiratory distress and, in some cases, death in humans.
Transmission:
- Hantavirus is spread through contact with the urine, feces, or saliva of infected rodents.
- It does not spread from person to person.
Types of Hantavirus Diseases
The two principal types of hantavirus diseases are:
Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS):
- Geographical Distribution: Primarily found in the Western Hemisphere, especially in North and South America.
- Primary Reservoir: Deer mouse.
- Clinical Manifestations: HPS is characterized by acute respiratory distress and fluid buildup in the lungs, leading to respiratory failure.
Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS):
- Geographical Distribution: Mainly reported in Europe and Asia.
- Clinical Manifestations: HFRS involves bleeding disorders and complications related to kidney function, potentially leading to kidney failure.
- Rodent Reservoir: Varies by region, depending on the specific rodent species responsible.
Symptoms of Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS):
Initial Symptoms (1-8 weeks post-exposure):
HPS typically begins with flu-like symptoms, including fatigue, fever, and muscle aches.Advancing Symptoms:
As the disease progresses, patients develop severe respiratory complications due to fluid buildup in the lungs, leading to difficulty breathing and respiratory failure.Mortality Rate:
Approximately 38% of patients with severe respiratory symptoms may die from HPS if not treated promptly.
Treatment and Management:
No Specific Cure or Vaccine:
Currently, there is no specific treatment, cure, or vaccine for HPS.Antiviral Medications:
Some antiviral medications may help alleviate symptoms but are not a cure for the virus.Supportive Care:
Early detection and hospitalization are critical. Respiratory support, such as the use of breathing tubes or ventilators, may be necessary for severe cases.
